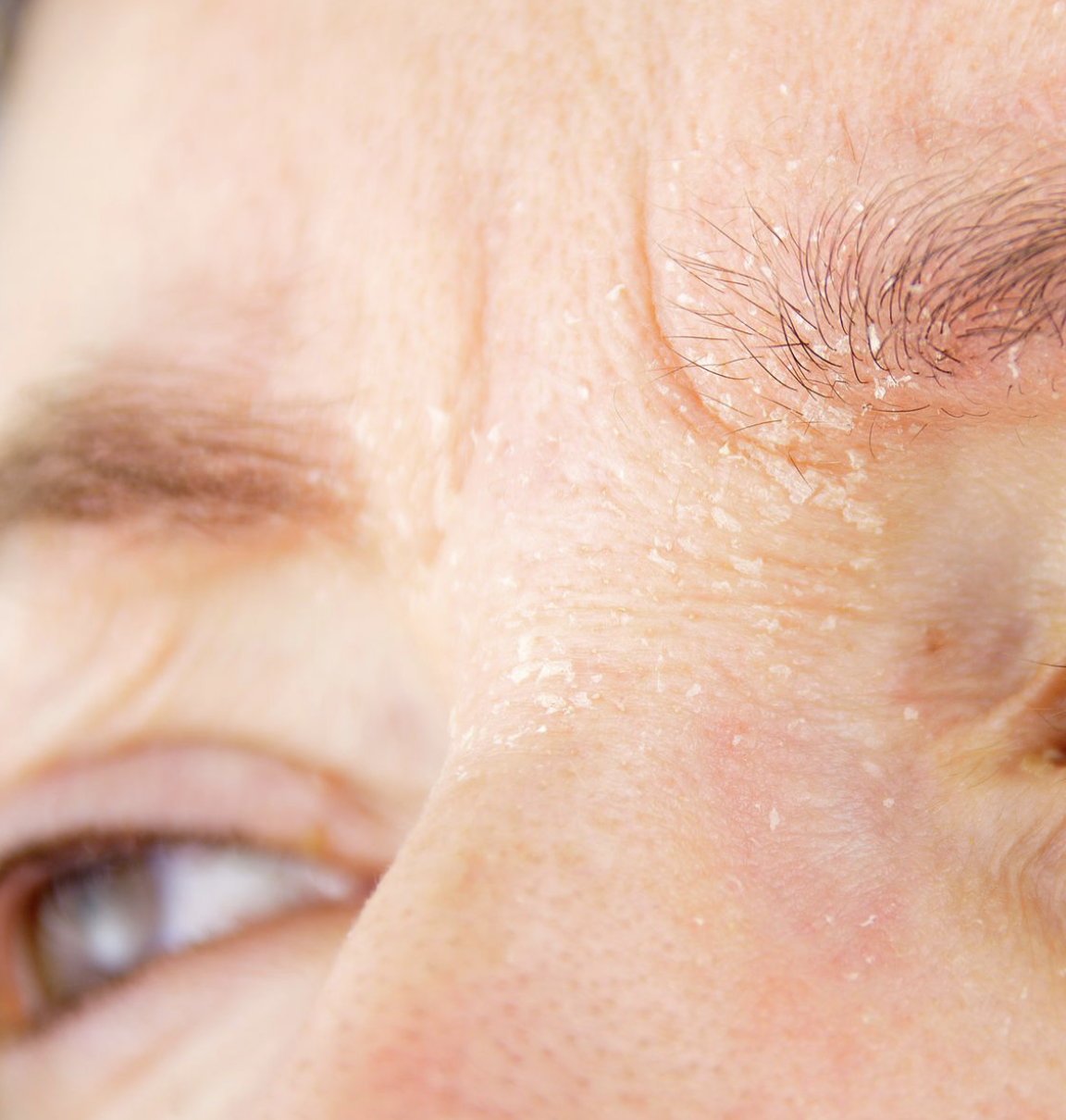
Living with eczema can be a challenging and often frustrating experience. The chronic skin condition is characterized by dryness, inflammation, itching, and a compromised skin barrier. Finding the right skincare routine to manage these skin condition symptoms and promote healthy, hydrated skin is essential for those affected by this condition.
What is eczema?
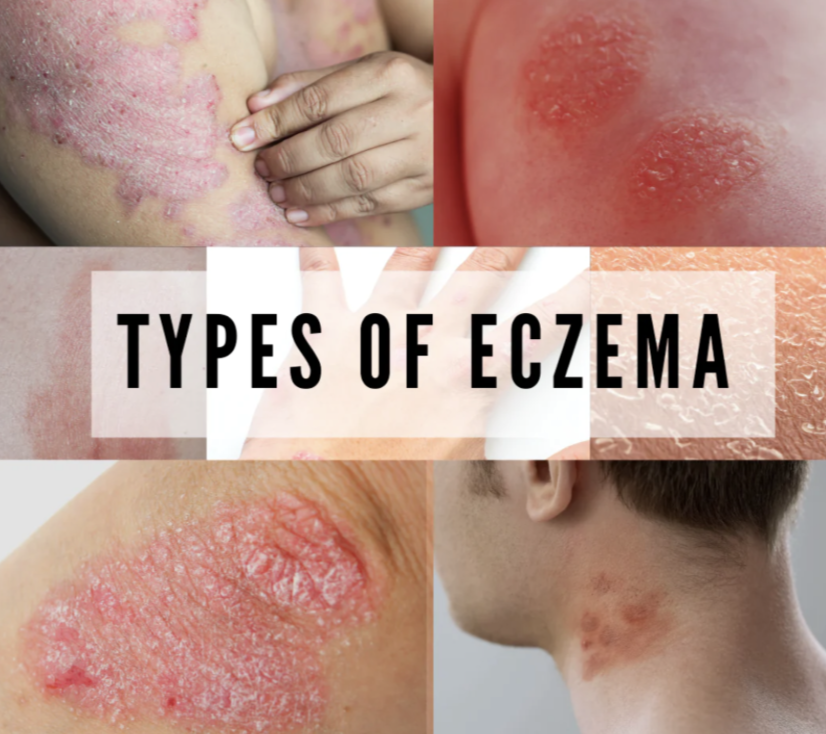
Eczema is a word used to represent a set of inflammatory skin disorders that cause rash-like symptoms, such as irritated, itchy spots on the skin, rather than a specific illness. There are a lot of types of eczema such as atopic, contact, dyshidrotic, nummular eczema and much more. Although clinically speaking, atopic dermatitis is the most common type of eczema, the terms “eczema” and “atopic dermatitis” are frequently used interchangeably. The most severe and persistent form of eczema is atopic dermatitis. It is characterised by swollen, inflammatory skin that may burst open when scratched and dripping clear fluid. According to the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, people with atopic dermatitis frequently have flare-ups, during which their symptoms get worse, and remissions, during which their symptoms get better or go away.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the world of skincare for eczema, providing you with the knowledge and tools to develop a complete skincare routine tailored to your specific needs.
There are also some common symptoms for all types of this skin condition:
- dry, scaly skin
- redness
- hyperpigmentation
- itching, which may be intense
Now, let’s look into the most three common ones:
Atopic eczema
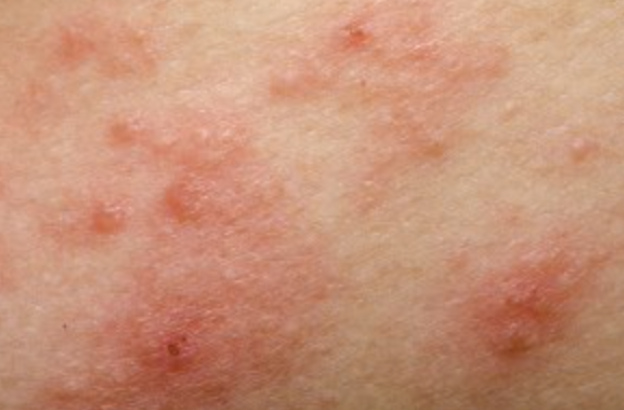
Symptoms:
- The rash frequently develops in the creases of your knees or elbows.
- The skin around the rash’s appearance may become thicker, lighter, or darker.
- If you scratch tiny pimples, fluid may escape from them.
- Babies frequently develop a rash on their cheeks and scalp.
- If you scrape your skin, an infection could develop.
Causes:
When your skin’s protective natural barrier from the elements is compromised, atopic dermatitis develops. As a result, you have less skin defence against irritants and allergens.
One or more of the following may contribute to atopic dermatitis:
- Genes cause dry skin
- The environment causes immune system issues
Contact eczema
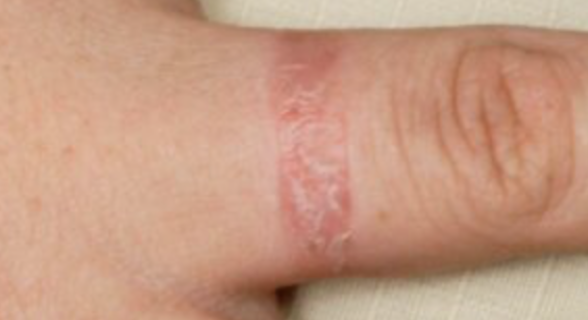
Symptoms:
- Your skin itches, turns red, is hyperpigmented or pink, magenta, burns, and stings.
- Itchy bumps called hives may appear on your skin.
- Fluid-filled blisters can form that may ooze and crust over.
- Over time, the skin may thicken and feel scaly or leathery.
Causes
Contact dermatitis happens when you touch a substance that irritates your skin or causes an allergic reaction. The most common causes are:
- detergents
- bleach
- jewellery
- latex
- nickel
- paint
- poison ivy and other poisonous plants
- skin care products, including makeup
- soaps and perfumes
- solvents
- tobacco smoke
Dyshidrotic eczema
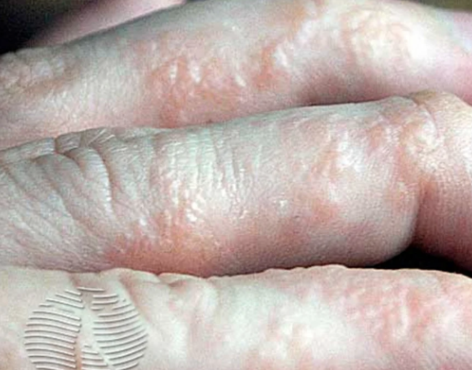
Symptoms:
- Your fingers, toes, palms, and foot soles develop fluid-filled blisters.
- These blisters could pain or irritate.
- Scales, cracks, and flakes might appear on your skin.
Causes
- Allergens sweaty feet and hands contact
- Metals like nickel, cobalt, or chromium stress from smoking tobacco products
Tips on the common treatments:
- Topical corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory medications are frequently used to lessen inflammation, redness, and itching. Stronger corticosteroids may be used for more severe flare-ups, while milder ones are appropriate for sensitive areas.
- Emollients and moisturisers: Keeping the skin moisturised and enhancing its barrier function are essential for treating this skin condition. Look for alternatives that are hypoallergenic, fragrance-free, and made especially for sensitive skin. After showering, use them freely as needed for the rest of the day. Moisturisers can be found here.
- Dressings and Wet Wraps: Wet wraps entail spreading a layer of moisturiser to the damaged skin and then covering it with wet or damp bandages or garments. This method relieves irritation while hydrating the skin and lowering inflammation.
- Antihistamines: By lowering the body’s response to histamine, antihistamines taken orally can help reduce itching and enhance the quality of sleep.
- Antibiotics: Topical or oral antibiotics may be administered to treat infections brought on by eczema or to treat bacterial colonisation to minimise swelling. It’s crucial to adhere to the recommended course and finish the entire term of treatment.
- Light therapy, often known as phototherapy, involves exposing the damaged skin to controlled doses of ultraviolet (UV) light, either from the sun or an artificial source.
Building a Safe Skincare Routine:
A. Facial Skin Cleansing
- Choosing the best formulation for gentle facial cleansers
- Steering clear of harsh ingredients and scents
- Effective cleaning methods for sensitive facial skin
B. Face Moisturising Techniques
- The Role of facial moisturisers in the Management of Eczema
- Hydration techniques: Timing and application for maximum benefit
- Choosing the best moisturiser for eczema-prone facial skin
- Applying facial oils and balms as protective layers
C. Sunscreen
- Recognising how sun exposure affects facial eczema
- Choosing facial sunscreens for sensitive skin
- Sun safety advice for faces at risk for eczema
D. Cosmetics & Skincare
- Minimising irritants and allergens when using makeup
- How to use skincare products: To read labels and avoid triggers
- Patch testing to ensure facial skin compatibility
E. Treatment
- Recognising triggers: keep a diary about the flare-ups
- Facial flare-up emergency care: comforting itching and inflammation
- Modifying your skincare routine during flare-ups
Products we recommend:
-
La Roche-Posay Toleriane Sensitive Double Repair Moisturiser
-
Dermalogica Active Moist Hydrating Oil-free Moisturiser
-
CeraVe Facial Moisturising Lotion PM Ultra Lightweight
-
La Roche-Posay Cicaplast Baume B5 Repairing Balm
-
Uriage Bariederm Repairing Cica Cream with Cu-Zn
-
Cetaphil Healthy Radiance Brightness Refresh Face Toner
-
Cetaphil PRO Night Cream
-
Cetaphil Daily Hydrating Face Moisturiser
-
CeraVe Hydrating Cleanser
References:
https://banish.com/blogs/article/7-types-of-eczema-and-its-symptoms
https://www.everydayhealth.com/eczema/guide/
https://nationaleczema.org/eczema/types-of-eczema/contact-dermatitis/
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/summer-finger-bumps#what-it-is
https://www.healthline.com/health/types-of-eczema#dyshidrotic-eczema
https://www.womenshealthmag.com/beauty/a32780408/dermatologist-eczema-skincare-routine/